Christoph C. F. Schinkel1• Bernhard Kirchheimer2• Stefan Dullinger2•Danny Geelen3• Nico De Storme3• Elvira Hörandl1
1.Department of Systematics, Biodiversity and Evolution of Plants (with Herbarium)University of Goettingen, Göttingen, Germany
2.Department of Botany and Biodiversity ResearchUniversity of Vienna, Vienna, Austria
3.Department of Plant Production, Faculty of Bioscience Engineering Ghent, University Ghent, Belgium
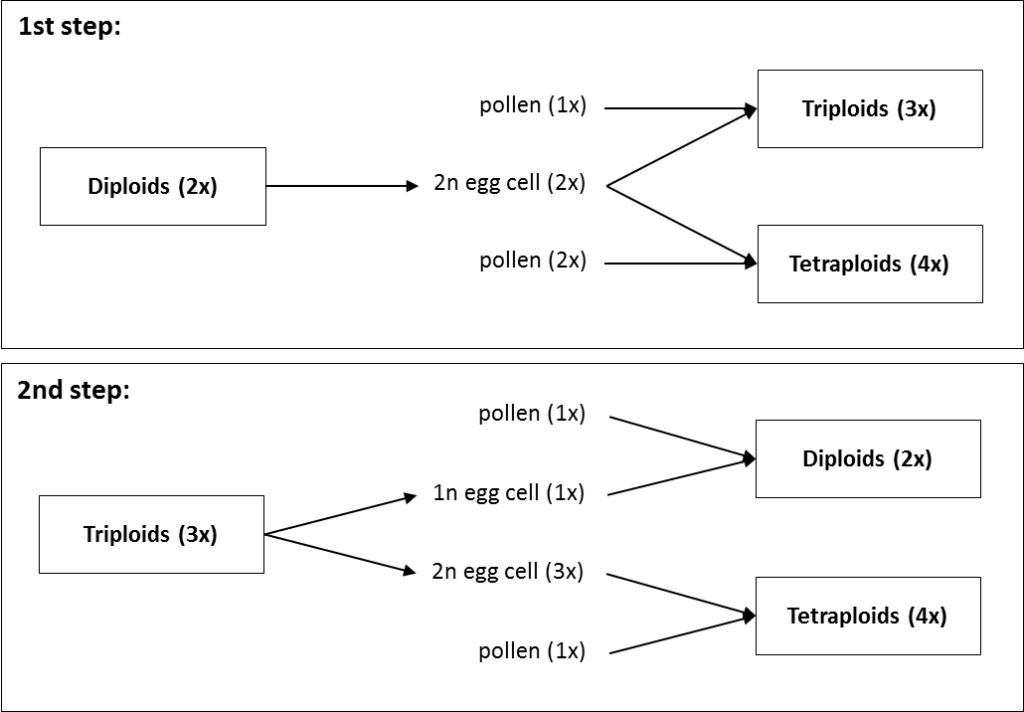
Polyploidy is one of the most important evolutionary processes in plants. In natural populations, polyploids usually emerge from unreduced gametes which either fuse with reduced ones, resulting in triploid offspring (triploid bridge), or with other unreduced gametes, resulting in tetraploid embryos. The frequencies of these two pathways, and male versus female gamete contributions, however, are largely unexplored. Ranunculus kuepferi occurs with diploid, triploid and autotetraploid cytotypes in the Alps, whereby diploids are mostly sexual, while tetraploids are facultative apomicts. To test for the occurrence of polyploidization events by triploid bridge, we investigated 551 plants of natural populations via flow cytometric seed screening. We assessed ploidy shifts in the embryo to reconstruct female versus male gamete contributions to polyploid embryo and/or endosperm formation. Seed formation via unreduced egg cells (BIII hybrids) occurred in all three cytotypes, while only in one case both gametes were unreduced. Polyploids further formed seeds with reduced, unfertilized egg cells (polyhaploids and aneuploids). Pollen was highly variable in diameter, but only pollen >27 μm was viable, whereby diploids produced higher proportions of well-developed pollen. Pollen size was not informative for the formation of unreduced pollen. These results suggest that a female triploid bridge via unreduced egg cells is the major pathway toward polyploidization in R. kuepferi, maybe as a consequence of constraints of endosperm development. Triploids resulting from unreduced male gametes were not observed, which explains the lack of obligate sexual tetraploid individuals and populations. Unreduced egg cell formation in diploids represents the first step toward apomixis.